My 1st WinOS K8 clusters
Categories:
2 minute read
Purpose
This page provides step-by-step instructions on how to bring online a simple test Kubernetes Cluster on Windows. So you can be one of the cool kids.
Prerequisites
- Windows Administrator privileges
- Chocolatey installed
General Information
Kubernetes is a platform which allows container based applications to follow cloud native practices via abstraction. The CNCF and community behind Kubernetes have done an excellent job steering the platform’s development the last 5 years with nearly major IT or Cloud vendors.
It maybe an oversimplification but I like to think of Kubernetes as having virtualised the core cloud technologies in the same way that VMWare’s vCentre virtualised Data Centers.
Instructions
Install Docker Desktop
-
Load up a command prompt or powershell with administrator privileges
-
Install Docker-desktop via chocolatey.
choco install -y docker-desktop
Enable Kubernetes in Docker Desktop
- Open the Docker Desktop settings.
- Click on the Kubernetes tab.
- Click on the Enable Kubernetes button, then Install if prompted and wait since this can take some time.
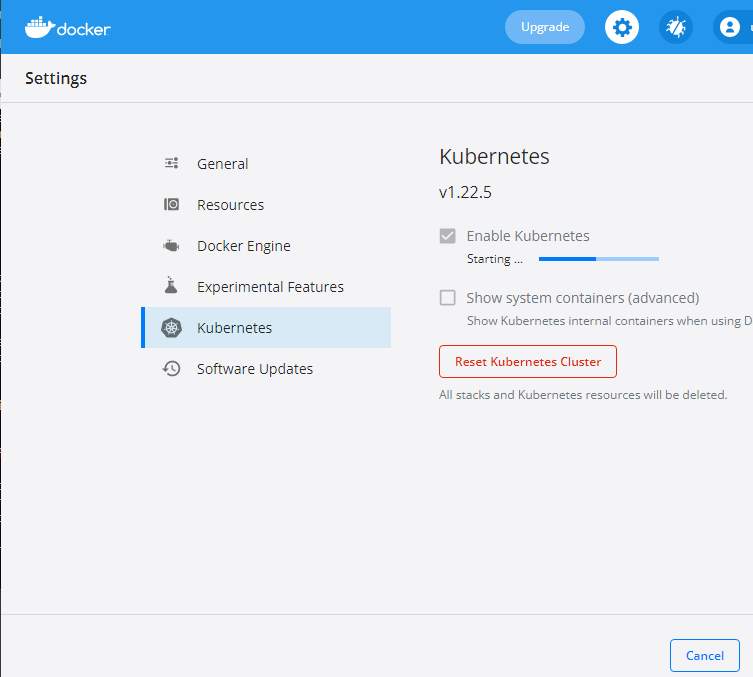
Connecting to Kubernetes Cluster
-
Install the Kubernetes CLI via Chocolatey, Kubectl.
- Open the command prompt or powershell with administrator privileges and run
choco install -y kubernetes-cli -
Check the kubectl is connected to the ‘docker-desktop’ cluster by running
kubectl config current-contextand that it can actually connect to the cluster by runningkubectl versionwhich will give you the version of the Kubernetes cluster.
The current context should be docker-desktop and a server version details should be returned.
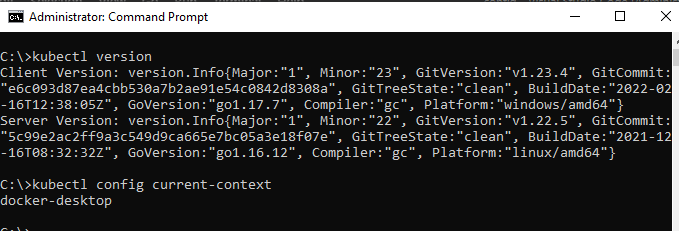
If this is the first time you have created a kubectl cluster on Windows it should work, but if you have previously connected to different clusters you may need to update your kubernetes connection file %HOMEPATH%\.kube\config or set context via kubectl config.
Note: If you plan on connecting to multiple Kubernetes clusters it is a good idea to keep your configuration file tidy (by deleting test clusters etc) and generally update it with good context names to allow for easy swapping between clusters. Since this configuration file is used by many tools and can quickly become messy if not maintained.
External Links
- Docker desktop official wiki instructions for more background information and screenshots.
- Kubernetes official documentation on connecting to different clusters.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Glad to hear it! Please email us tell us how we can improve, feedback@quarryfox.com.
Sorry to hear that. Please email us tell us how we can improve, feedback@quarryfox.com.